Binary Search
Binary Search in C#
Binary search also known as half-interval search , logarithmic search or binary chop
- is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
Binary search algorithm checks if the index "start" is greater than the index "end". Based on the value present at the variable "mid", the function is called again to search for element.
In other words binary search:
-
comparing an element in the middle of the array with the target value.
- if the target value matches the element, its position in the array is returned.
- If the target value is less than the element, the search continues in the lower half of the array.
- If the target value is greater than the element, the search continues in the upper half of the array.
- By doing this, the algorithm eliminates the half in which the target value cannot lie in each iteration.
Binary Search is a search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
Ginen:
-
Array $X^{n-1 (elements)}_{0}$ sorted such as
- \(X_{0} \le X_{1} \le X_{2} \le \dots \le X_{n - 1}\) and terget value \(T\) let's find value \(T\) in \(X^{n-1 (elements)}_{0}\)
-
set \(S\) as start_index, \(0\) and \(E\) as end_index, \(n - 1\).
- if \(E \ge S\). \(set:\) mid_index, \(m\) as \(S + \frac{(E - S)}{2}\).
- if \(X_{m} = T\). \(then:\) return mid_index, \(m\).
- if \(X_{m} > T\). \(set\) end_index, \(E\) to \(m - 1\)
- if \(X_{m} \le T\). \(set\) star_index, \(S\) to \(m + 1\)
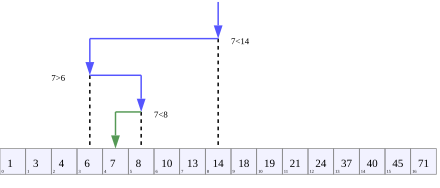
None:
- While it is possible to perform binary search using for-loop> and compare each number, the sequential search (binary search) is efficient, especially if the list is long.

#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int bsearch(int arr[], int S, int E, int T); int main(){ //Array int arr[]={1,3,4,6,7,8,10,13,14,18,19,21,24,37,40,45,71}; //size of array int n=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int); //number we are to searche (element, n) //we ask user to enter the number int T; printf("Enter Element: T to find in the Array: "); scanf("%d", &T); //start_index, S int S=0; //end_index, E int E=n - 1; //initialize the index we are searching for to the binary search implementation int index=bsearch(arr, S, E, T); /* if binary search (bsearch() function) return -1, - this means it did not find the number you are searching in the Array else, it will return the index of the searched number, (element, T). */ if (index == -1) { printf("Element T: %d is Not found.\n", T); }else { printf("Element, T: %d is found at index: %d",T, index); } return 0; }
This is the bsearch() function.
int bsearch(int arr[], int S, int E, int T){ //if end_index, E is greater or equal to start_index, S if (E >= S) { //find the middle_index, m int m= S + (E - S)/2; /* if array element at middle_index, m is equal to element, T(number we are finding) return the middle_index, m and end the program */ if (arr[m] == T){ return m; } /* if array element at middle_index, m is greater than element, T(number we are searching) return this function (bsearch() function) with end_index, E is set to middle_index, m - 1 else return this function (bsearch() function) with start_index, S is set to middle_index, m + 1 */ if (arr[m] > T){ return bsearch(arr, S, m - 1, T); }else { return bsearch(arr, m + 1, E, T); } } /* return -1 if the number we are searching (element, T) is not found in Array */ return -1; }